The interest in 5G and mIoT is exploding. It's exciting to see so many IT and cybersecurity professionals in my network trying to learn...
For many end-users of today's communications technology, the cloud is a somewhat mystical concept, a digital equivalent of aether. Most think of it as...
There are many adjectives that could be used to describe the global outbreak of COVID-19, but perhaps the simplest might be: fast.
The disease has...
Depending on who you speak to, 5G is either humankind’s greatest imminent blessing or its greatest imminent curse. Still in its infancy, and not...
In their outstanding book, Wicked and Wise, Alan Watkins and Ken Wilber look at some of the most pressing ‘wicked problems’ facing the human...
The human will to innovate is seemingly relentless. The history of our species is one of continual development, with the last 350 years, in...
In 1967, Lynn Margulis, a young biologist, published a paper that challenged more than a hundred years of evolutionary theory. It proposed that millions...
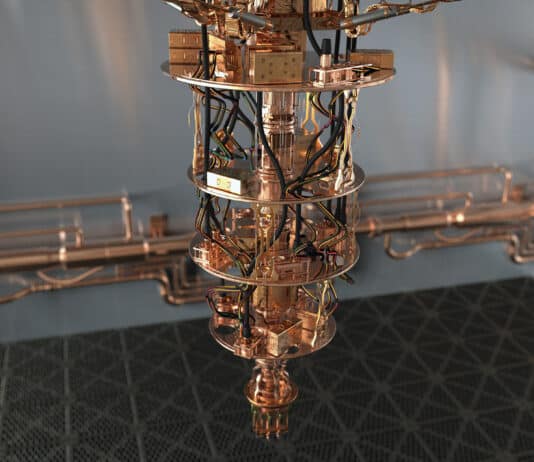
The secret sauce of quantum computing, which even Einstein called "spooky," is the ability to generate and manipulate quantum bits of data or qubits. Certain computational tasks can be executed exponentially faster on a quantum processor using qubits, than on a classical computer with 1s and 0s. A qubit can attain a third state of superimposition of 1s and 0s simultaneously, encode data into quantum mechanical properties by "entangling" pairs of qubits, manipulate that data and perform huge complex calculations very quickly.
The timeline of human history is marked by inflection points of major technological advancement. The plow, the printing press, the telegraph, the steam engine,...
In my previous post I argued that if Canada wants to succeed with its AI-focused innovation agenda, it should also be at the forefront...
If you've ever been to an expensive restaurant and ordered a familiar dish like, say, lasagna, but received a plate with five different elements...
Because it demands so much manpower, cybersecurity has already benefited from AI and automation to improve threat prevention, detection and response. Preventing spam and identifying malware are already common examples. However, AI is also being used – and will be used more and more – by cybercriminals to circumvent cyberdefenses and bypass security algorithms. AI-driven cyberattacks have the potential to be faster, wider spread and less costly to implement. They can be scaled up in ways that have not been possible in even the most well-coordinated hacking campaigns. These attacks evolve in real time, achieving high impact rates.
In 2013, George F. Young and colleagues completed a fascinating study into the science behind starling murmurations. These breathtaking displays of thousands – sometimes...
Not even 30 years separate us from the end of the Cold War. Yet, we appear to be witnessing the emergence of a new...
Emerging Technology and Geopolitics of 5G
There are several reasons emerging technology is a highly competitive industry, notwithstanding the race for intellectual property that can...